
The Challenge of Data Access Control
When setting up a business intelligence solution for your company, you’ll face a crucial challenge: your database and dashboards contain vast amounts of information, but not all users should have access to everything. To address this, Power BI offers Row-Level Security (RLS), a feature that restricts data access for certain users by defining filters at the row level within a dataset. This allows report authors to control which users can view specific rows of data based on their roles or group memberships.
Benefits of Row-Level Security
RLS is an essential component of a robust, compliant, and scalable data governance strategy, which proves itself valuable to any organization using Power BI in the following ways:
- In applications serving cross-functional users, RLS ensures that each client or department only sees their own data or data authorized to be shared across different business functions. For example, operations can see the results of a metric involving the cost of labor data, without seeing sensitive HR information such hourly salary.
- A single report can be configured to display different data and visuals depending on the user’s access level. This reduces reporting asset sprawl and development costs, eliminating the need to create separate reports for different user groups. For example, a report displaying the entire organization’s sales pipeline can be created, but sales reps only see the reporting on their own territory.
- RLS facilitates a centralized approach to data governance, allowing access settings to be modified in one place. This minimizes maintenance effort and ensures consistency across the organization.
Understanding the Key Components of RLS
Creating a robust RLS process involves careful planning and execution, and includes following a series of steps:
Step 1: Defining Roles
Roles are the foundation of your security model in Power BI. Think of roles as security profiles that represent different types of users in your organization. You can create multiple roles to match your organization’s structure – for example, “Regional Managers,” “Department Heads,” or “External Clients.” When planning roles, consider your organization’s hierarchy, departmental boundaries, and data access requirements. The key is to create roles that align with your business’s natural segmentation of data access needs.
Step 2: Define Filters
Filters are the rules that determine what data each role can see. These are the actual security conditions that are evaluated by Power BI when users access reports. You can create filters using simple dropdown selections or advanced DAX formulas for more complex scenarios. For instance, you might create filters that:
- Limit regional managers to seeing only their territory’s data
- Allow department heads to view their department’s data in detail, plus summary data from other departments
- Restrict external clients to viewing only their own account information
Step 3: Assigning Users
User assignment is the final RLS step and connects your actual users (identified by their email addresses or security groups) to the roles you’ve created. You can assign users individually or use security groups for easier management. This flexibility allows you to efficiently manage access as your organization grows or changes. Consider using security groups for easier maintenance, especially in larger organizations where user turnover is.
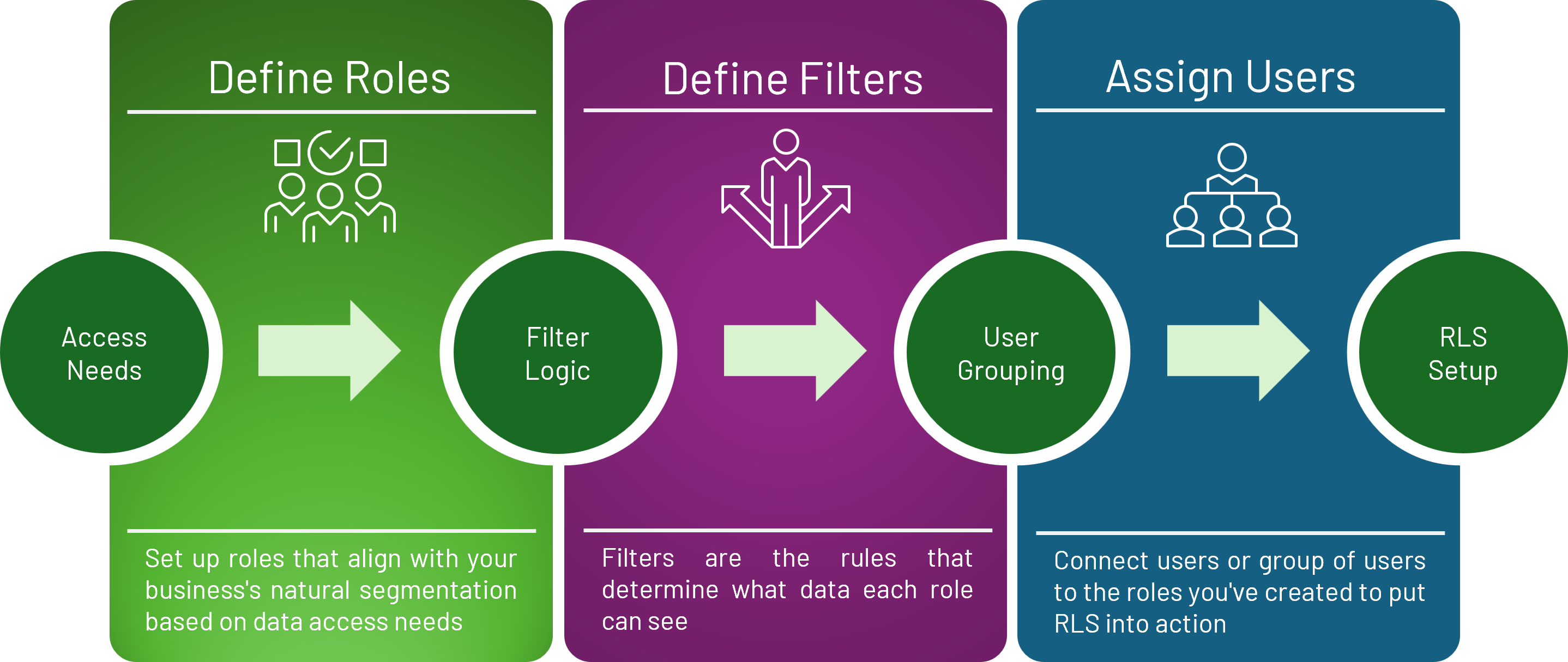
Exhibit A.: The key components of Row-Level Security (RLS) and the steps needed to execute it.
Technical Implementation
To implement RLS in your Power BI environment, the following steps are needed:
- In Power BI Desktop:
- Navigate to the Modeling tab and select Manage Roles
- Create new roles and define their data access rules
- Use either the visual editor or DAX formulas to set up filters
- In Power BI Service:
- Publish your RLS-enabled report
- Navigate to the workspace containing your semantic model
- Under Security settings, assign users or security groups to roles
Conclusion
Row-Level Security is more than just a technical feature —it’s a fundamental component of a comprehensive data governance strategy. When implemented thoughtfully, RLS enables organizations to:
- Maintain data security while promoting data-driven decision making
- Scale their BI solution efficiently without compromising security
- Reduce development and maintenance overhead through centralized security management
- Meet compliance requirements by ensuring appropriate data access controls
By taking time to properly plan your RLS implementation – carefully considering your roles, designing appropriate filters, and managing user assignments – you can create a secure, scalable, and maintainable business intelligence environment that serves your organization’s needs while protecting sensitive information.




